In this article, we aim to demystify the working principles behind oxygen generators, diving deep into their functionality and exploring how air, a mixture of gases, is methodically turned into a concentrated stream of life-supporting oxygen. Let’s embark on this captivating journey of knowledge to comprehend the underpinnings of a technology that, in many aspects, forms the bedrock of our modern, dynamic world.
What is an oxygen generator?
What is an Oxygen Generator Used For?
An industrial oxygen generator is a powerful tool used in various commercial settings to produce a concentrated supply of oxygen. It excels both in healthcare environments and a broad spectrum of industries. In healthcare settings, such as hospitals, they supply oxygen for patients and medical procedures. Industrial sectors such as metallurgy, chemical manufacturing, waste treatment, and water treatment also rely heavily on these generators; they use oxygen to enhance combustion processes, facilitate chemical reactions, and manage waste. Therefore, an oxygen generator’s primary role lies in enhancing the efficiency, sustainability, and productivity of a wide range of processes in diverse sectors.
Difference between Oxygen Concentrator and Oxygen Concentrator
The difference between an oxygen concentrator and an oxygen generator is subtle, but significant. Primarily used in medical settings and home healthcare, an oxygen concentrator takes in ambient air, filters out nitrogen, and delivers purified oxygen to the user. It’s primarily designed for individual use, ensuring a continuous oxygen supply for patients with respiratory conditions.
On the other hand, an oxygen generator operates on a much larger scale, often implemented in industrial settings. While it uses the same principle of separating oxygen from nitrogen, the primary difference lies in the output. Industrial oxygen generators are high-capacity machines built to produce large volumes of concentrated oxygen, serving various industries like steel manufacturing, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment. They are more robust, durable, and capable of fulfilling high-demand oxygen requirements.
Oxygen Generator Applications
The applications of industrial oxygen generators span across numerous industries, contributing to the efficiency and productivity of many industrial processes.
- Steel and Metal Industry: Enhances combustion in furnaces for efficient heating and precision cutting of metals. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces fuel consumption and costs.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Facilitates numerous chemical reactions leading to the production of important compounds, improving efficiency and yield.
- Waste and Water Treatment: Used in oxidation processes to help break down pollutants, creating a cleaner environment.
- Glass and Ceramics Industry: Improves furnace efficiency and the quality of the final product.
- Mining Sector: Assists in the extraction of precious metals like gold, copper, zinc, and others from their ores.
- Aquaculture: Maintains optimal oxygen levels in water tanks, crucial for the health and growth of aquatic life, leading to more productive farming.
How does Oxygen Generator Work
Oxygen generators separate oxygen from other components in the air, primarily nitrogen. A variety of methods can be used, each with its unique approach and application. Here are the most prominent ones.
Cryogenic Distillation Separation
Cryogenic distillation leverages the different boiling points of gases found in air. By cooling the air to subzero temperatures, different gases liquify at different stages. Oxygen, having a boiling point of -183°C, converts into a liquid before nitrogen and can thus be separated. This process produces a high purity of up to 99.9995% oxygen but requires significant energy input and is generally employed in high-volume industrial scenarios.
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)
Pressure Swing Adsorption is a prevalent method used in both commercial and medical oxygen generators. It uses zeolite, a material with a large surface area that preferentially adsorbs nitrogen from the air at high pressure. When the pressure is reduced, the nitrogen is released, leaving behind a high concentration of oxygen. PSA is cost-effective and efficient, providing an oxygen purity of up to 99.5%.

Membrane Separation
Membrane separation involves forcing air under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane. The membrane allows oxygen to pass through more readily than nitrogen and other gases, thereby effectively concentrating the oxygen. This method is particularly cost-effective and easy to maintain but generally yields a lower oxygen purity of around 90-95%.
Chemical Oxygen Production
Chemical oxygen production relies on chemical reactions to generate oxygen. For instance, heating potassium chlorate (KClO3) leads to the release of oxygen. Although capable of producing high-purity oxygen, this method is not typically used for large-scale production due to safety concerns and high costs.
Water Electrolysis
Water electrolysis involves passing an electric current through water to split it into hydrogen and oxygen. This method can produce very high purity oxygen, although the cost and energy inputs can be significant. It’s often utilised in space applications where water is available and electric power is abundant.
Each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages, making each more suitable to certain applications than others. Today’s advancements aim to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of these processes, opening up new possibilities for oxygen generation.
Types of oxygen generators
Oxygen generators vary greatly based on several factors such as oxygen purity, production volume, application, production principle, and more. Below, we’ll explore the different types of oxygen generators according to these categories.
Divided by Oxygen Purity
Oxygen generators can be categorized by the purity of the produced oxygen:
- Low Purity Oxygen Generators: These generators produce oxygen with a lower concentration, typically around 90%-95%. They are mostly employed in applications where high purity isn’t a requirement, such as in some aquaculture or pneumatic device usage.
- High Purity Oxygen Generators: These machines are designed to generate oxygen with purities up to 99.5% or more, and are used when higher oxygen concentrations are needed. Medical and industrial applications often require high purity oxygen.
Only the Production of Oxygen or Production of Oxygen and Nitrogen
There are generators designed for:
- Oxygen-Only Production: These generators are designed exclusively to capture and condense oxygen from the air.
- Oxygen and Nitrogen Production: Some machines can help extract both oxygen and nitrogen simultaneously. They are beneficial in industries that utilize both gases, like certain manufacturing and chemical processes.
Divided by Oxygen Production Volume
Based on the volume of oxygen produced, you have:
- Small Scale Oxygen Generators: These units are designed for applications with lower oxygen requirements, such as small health clinics or personal use.
- Industrial Scale Oxygen Generators: These are larger machines that produce a high volume of oxygen, commonly implemented in industries like steel manufacturing, glass production, and chemical processing.
Divided by the Principle of Oxygen Production
Oxygen generators also vary by the method they use to separate and concentrate oxygen:
- PSA Oxygen Generators: These generators use the Pressure Swing Adsorption technique.
- Membrane Oxygen Generators: These use a semi-permeable membrane to separate oxygen.
- Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: These utilize the cryogenic distillation principle for oxygen separation.
Divided by Working Pressure
Generators can also be grouped according to their working pressure:
- Low Pressure Oxygen Generators: These systems operate at pressures up to 5 bar. They are suitable for applications that do not require high-pressure oxygen feed, such as waste and water treatment or in some fish farming methods.
- High Pressure Oxygen Generators: These systems produce oxygen at pressures of 20 bar or more, often for medical or industrial purposes requiring high pressure.
Components of an Oxygen Generator
Understanding the components of an oxygen generator is critical to comprehending this equipment’s functionality. Let’s delve into the main parts that make up an oxygen generator:
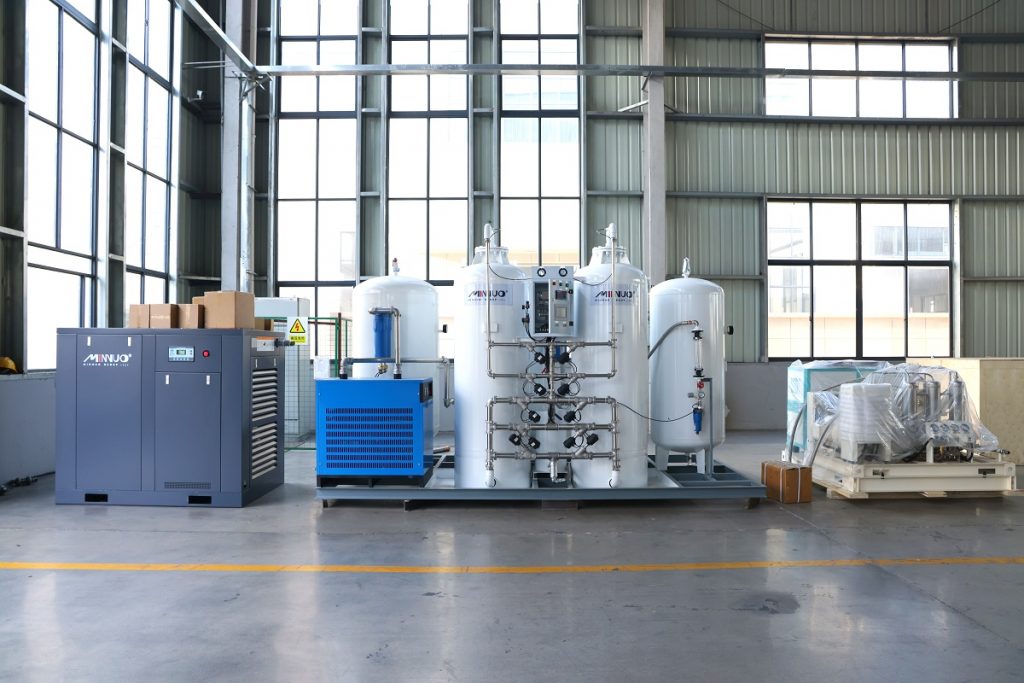
Air Compressor
The air compressor forms the first significant component, sourcing air for the oxygen generator. It compresses ambient air and delivers it under pressure to the following stages of the generator. This process aids in the effective separation of oxygen from other gases present in the air.
Air Prep/Filtration
Once the air is compressed, it moves to the air prep or filtration stage, where it is cleaned and dried. This system typically consists of a combination of filters and air dryers. They remove dust, oil, water vapor, and other impurities from the compressed air before moving to the separation module. This step is critical to prevent possible damage to the sieve beds where the separation process occurs.
Oxygen Separation Unit
The oxygen separation unit, which could be a PSA module, a membrane separator, or a cryogenic unit, represents the heart of an oxygen generator. This component separates the oxygen from the surrounding air, based on the separation method of the particular generator.
In a PSA-based oxygen generator, the separation unit consists of the sieve beds (filled with zeolite material) and a set of valves managing the pressure cycling. In a membrane-based separator, it’s a semi-permeable membrane that discriminates against nitrogen and other gases. And in a cryogenic unit, it involves a complex series of heat exchangers and distillation columns that cool, liquify, and separate the air components.
Oxygen Buffer Tank
After the separation process, the generated oxygen usually enters an oxygen buffer tank. This tank serves as temporary storage, smoothing out any variations in output flow or concentration and ensuring there’s always a ready supply of oxygen that can be drawn upon as needed.
Controls and Monitoring System
A controls and monitoring system manages the operation of the generator and keeps an eye on its performance. It may include pressure gauges, flow meters, oxygen concentration sensors, control valves, and a control panel incorporating manual or automated operations. This system not only ensures the safety and efficiency of the oxygen generator but also provides critical real-time information to the users about the system performance.
Together, these components form an integrated oxygen generator system, each playing a vital role in delivering concentrated oxygen for a wide variety of applications. Understanding these components will aid in the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of oxygen generators.
Are Oxygen Generators Safe?
Oxygen generators, robust devices frequently used in industries and healthcare settings, are generally safe to use with proper handling and regular maintenance. Their safety largely depends on adherence to guidelines such as keeping the equipment away from open flames or flammable substances due to oxygen’s combustion-enhancing properties, and correctly following operational specifications respective to different models.
These devices often come equipped with safety features such as alarms, warning systems, and automatic shut-off mechanisms to prevent hazards related to oxygen purity, pressure variations, or system failures. Regular maintenance, including changing filters, adjusting pressures, and inspecting for potential leaks, further contributes to safety by ensuring robust function and preventing malfunctions.
Regardless of their inherent safety measures, their usage should comply with local regulations and best practices. While oxygen generators are a vital tool in many industries and for individuals needing additional oxygen, they should not replace professional medical care for individuals with respiratory conditions. Understanding the characteristics of these devices will ensure their safe and beneficial use.
How do I Buy an Oxygen Generator?
Purchasing an oxygen generator involves several steps that will guide you to the most suitable equipment for your needs.
Firstly, you need to clearly identify your specific needs. These might be influenced by variables such as the volume of oxygen required, the required purity levels, electricity consumption, geographical location, and local regulations.
For instance, in the healthcare sector, patients’ requirements might depend on their specific health conditions and doctor’s advice, whereas, for industry use, it’s often about the volume and degree of oxygen purity needed for specific processes.
Once you’ve established your requirements, thorough research is pivotal. Begin by selecting reliable suppliers or manufacturers, considering both their reputation and product range. Check customer reviews, get referrals from industry peers, or consult your healthcare provider. Other important factors to consider when choosing a supplier include after-sales service, warranty terms, and availability of spare parts. You should also ensure that the products adhere to international safety and quality standards.
Once you’ve narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed product specifications, pricing, and delivery options. You may want to compare several different models or suppliers to find the most cost-effective solution that meets your needs. Ask about installation, maintenance, and operating costs for an accurate assessment of total cost of ownership.
Finally, before making a purchase, confirm the payment options, shipping, and delivery terms. For large industrial generators, find out if installation assistance is offered. And, especially in the case of healthcare use, it’s essential to understand how to operate the generator safely and efficiently.
In summary, understanding your needs, conducting thorough research, comparing options, and confirming purchase and delivery details are critical steps that will help you make an informed decision when buying an oxygen generator.