In today’s medical and industrial sectors, oxygen generators have become indispensable. Whether it’s helping patients with breathing difficulties or providing essential oxygen supply in industrial processes, understanding how these devices work is crucial. But how exactly do oxygen generators operate?
Oxygen generators use a unique selective adsorption technology to separate oxygen from nitrogen and other components in compressed air, producing high-purity oxygen. This technology is widely used in both medical and industrial fields, ensuring a continuous supply of pure oxygen.
If you’re considering purchasing an oxygen generator or are simply curious about its mechanism, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive explanation.
What is an Oxygen Generator
Oxygen generator is a kind of machine that can make oxygen, which utilizes air separation technology to extract oxygen from air, all also known as air separation equipment.
- According to the working principle, it can be divided into: PSA Oxygen Generator, Cryogenic Oxygen Generator, Electrolyzed Water Oxygen Generator, Oxygen Enriched Membrane Oxygen Generator.
- According to the application scenario, they can be divided into: industrial oxygen generator, household oxygen generator, medical oxygen generator.
What is an Oxygen Generator Used For?
An industrial oxygen generator is a powerful tool used in various commercial settings to produce a concentrated supply of oxygen. It excels both in healthcare environments and a broad spectrum of industries. In healthcare settings, such as hospitals, they supply oxygen for patients and medical procedures. Industrial sectors such as metallurgy, chemical manufacturing, waste treatment, and water treatment also rely heavily on these generators; they use oxygen to enhance combustion processes, facilitate chemical reactions, and manage waste. Therefore, an oxygen generator’s primary role lies in enhancing the efficiency, sustainability, and productivity of a wide range of processes in diverse sectors.
Oxygen Generator vs. Oxygen Concentrator
The difference between an oxygen concentrator and an oxygen generator is subtle, but significant. Primarily used in medical settings and home healthcare, an oxygen concentrator takes in ambient air, filters out nitrogen, and delivers purified oxygen to the user. It’s primarily designed for individual use, ensuring a continuous oxygen supply for patients with respiratory conditions.
On the other hand, an oxygen generator operates on a much larger scale, often implemented in industrial settings. While it uses the same principle of separating oxygen from nitrogen, the primary difference lies in the output. Industrial oxygen generators are high-capacity machines built to produce large volumes of concentrated oxygen, serving various industries like steel manufacturing, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment. They are more robust, durable, and capable of fulfilling high-demand oxygen requirements.
How Does an Oxygen Generator Work
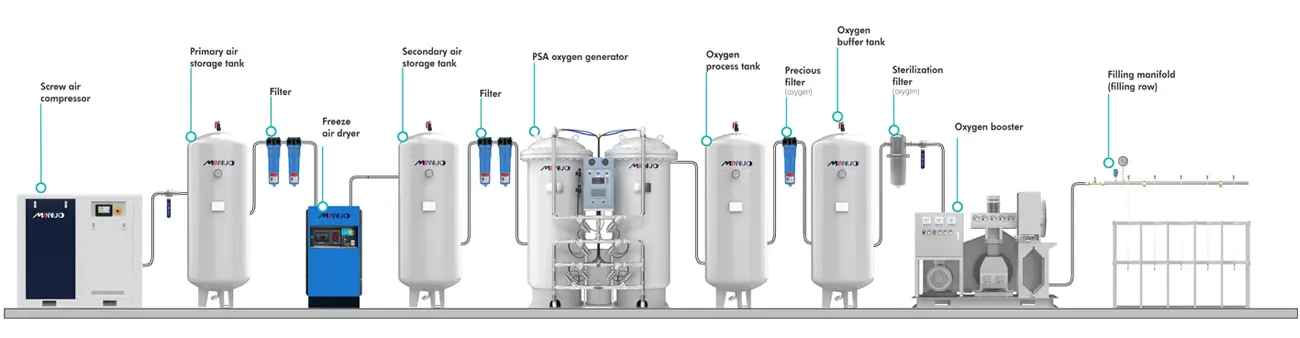
Air consists mainly of nitrogen (about 78%) and oxygen (about 21%), with small amounts of other gases also included. The core principle of an oxygen generator is based on the difference between the molecular size and molecular weight of the nitrogen and oxygen molecules in the atmosphere to obtain a purer form of oxygen, usually with a purity of over 90%. This article focuses on how PSA oxygen generators work.
PSA oxygen generator
We operate PSA oxygen generating equipment, also known as variable pressure adsorption oxygen generating equipment, to obtain higher purity oxygen (93% ± 2). At normal temperature and pressure, we use the PSA special molecular sieve to selectively adsorb nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor, which are impurities in the air. Our main working principle involves two molecular sieve adsorption towers. At room temperature, we introduce compressed air that has undergone filtration, dewatering, and drying into the adsorption tower. Inside the tower, nitrogen and other impurities are adsorbed by the molecular sieve, enriching the oxygen in the gas phase, which then exits through the oxygen buffer tank for storage. Meanwhile, the molecular sieve in the other tower, which has completed adsorption, undergoes rapid depressurization to release the adsorbed components. By alternating cycles between the two towers, we can consistently produce inexpensive oxygen of purity (93% ± 2).
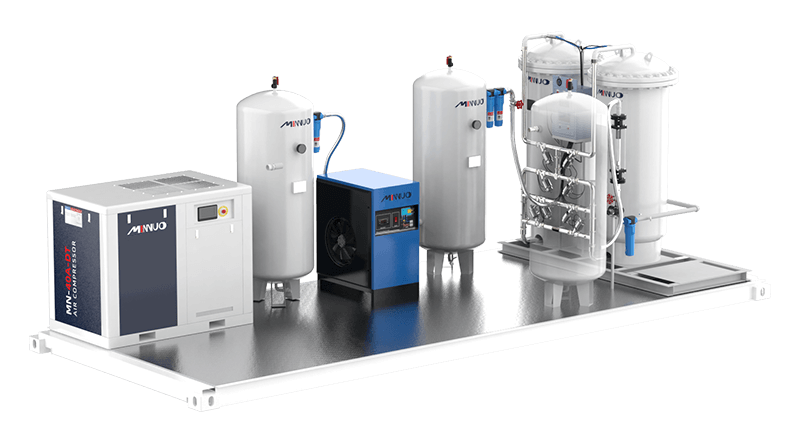

Cryogenic Oxygen Generator
A technology that separates air through a deep freezing and distillation process to prepare oxygen. We actively cool the air to a temperature below 100 K in the deep freezing process to liquefy it. We then exploit the difference in boiling points of oxygen and nitrogen at atmospheric pressure—90 K for oxygen and 77 K for nitrogen—to make nitrogen, which has a lower boiling point, vaporize more readily than oxygen. In the distillation tower, the higher temperature of the vapor and the lower temperature of the liquid constantly in contact with each other, more nitrogen in the liquid evaporates, more oxygen in the gas condenses, so that the nitrogen content in the ascending vapors continues to improve, and the oxygen content in the downstream liquid continues to increase, in order to achieve the separation of the air, the production of high purity oxygen.
Electrolyzed water oxygen generator
The electrolyzer decomposes water into hydrogen and oxygen. During the electrolysis process, a power source provides electrical energy to break down water in the electrolyzer. We chemically perform the process known as water electrolysis, which results in the production of hydrogen and oxygen. We discharge hydrogen through a drainage unit and deliver oxygen to the required location through an air supply unit.
Oxygen Enriched Membrane Oxygen Generator
We utilize a special membrane material, known as an Oxygen Enriched Membrane, to actively separate oxygen from the air for the purpose of oxygen production. Oxygen-enriched membrane is a special membrane material with a high concentration of oxygen molecules inside, which can selectively allow oxygen to pass and prevent other gases from passing.
Oxygen generators of different types have different working principles, so after selecting the oxygen generator, you can choose according to the purity of oxygen, flow rate and application scenarios and so on. If the selection is difficult, you can contact us!
Chemical Oxygen Production
Chemical oxygen production relies on chemical reactions to generate oxygen. For instance, heating potassium chlorate (KClO3) leads to the release of oxygen. Although capable of producing high-purity oxygen, this method is not typically used for large-scale production due to safety concerns and high costs.
Components of an Oxygen Generator
Understanding the components of an oxygen generator is critical to comprehending this equipment’s functionality. Let’s delve into the main parts that make up an oxygen generator:
Air Compressor
The air compressor forms the first significant component, sourcing air for the oxygen generator. It compresses ambient air and delivers it under pressure to the following stages of the generator. This process aids in the effective separation of oxygen from other gases present in the air.
Air Prep/Filtration
Once the air is compressed, it moves to the air prep or filtration stage, where it is cleaned and dried. This system typically consists of a combination of filters and air dryers. They remove dust, oil, water vapor, and other impurities from the compressed air before moving to the separation module. This step is critical to prevent possible damage to the sieve beds where the separation process occurs.
Oxygen Separation Unit
The oxygen separation unit, which could be a PSA module, a membrane separator, or a cryogenic unit, represents the heart of an oxygen generator. This component separates the oxygen from the surrounding air, based on the separation method of the particular generator.
In a PSA-based oxygen generator, the separation unit consists of the sieve beds (filled with zeolite material) and a set of valves managing the pressure cycling. In a membrane-based separator, it’s a semi-permeable membrane that discriminates against nitrogen and other gases. And in a cryogenic unit, it involves a complex series of heat exchangers and distillation columns that cool, liquify, and separate the air components.
Process Flow of Oxygen Generator Work
- Compression: First, we actively draw air into the variable pressure adsorption oxygen generator and subsequently compress it. The pressure of the compressed air increases, but it still contains a large amount of nitrogen and a small amount of oxygen.
- Adsorption: The compressed air enters the molecular sieve adsorption tower. We operate the molecular sieve adsorption tower under high pressure, where the molecular sieve selectively adsorbs oxygen from the air, leaving the nitrogen unadsorbed.
- Pressure reduction: When the molecular sieve adsorption tower has adsorbed a certain amount of oxygen, we stop the air supply to the tower and begin reducing its pressure. During the pressure reduction process, we desorb the adsorbed oxygen, forming high purity oxygen.
- Recovery: The desorbed oxygen goes through the recovery pipeline into the gas storage tank and is output as a product. Meanwhile, the pressure of the molecular sieve adsorption tower continues to decrease until it is close to atmospheric pressure.
- Regeneration: We perform regeneration by reducing the pressure of the molecular sieve adsorption tower to near atmospheric pressure, which discharges the remaining nitrogen from the tower and regenerates the molecular sieve. During the regeneration process, the molecular sieve will absorb the oxygen in the new air, ready to enter the next cycle.
This cycle can realize the purpose of continuous oxygen production, so that users can choose the right oxygen generator for themselves at the same time can also improve the efficiency of oxygen production and reduce the cost of oxygen production.
Oxygen Generator Applications
Oxygen generators have a wide range of applications in a variety of fields, some of the main areas include:
- Medical use: Oxygen generators are used in hospitals, clinics and home healthcare to provide high purity oxygen to patients. This oxygen is used in the treatment of respiratory diseases, surgery, first aid and oxygen therapy.
- Industrial use: Oxygen generator is widely used in industrial process such as oxygen cutting, oxygen welding, ore smelting, oil refining, glass manufacturing and metal processing.
- Food processing: Oxygen generator is used in food processing industry, such as in food packaging to prevent food from rotting and maintain the freshness of food.
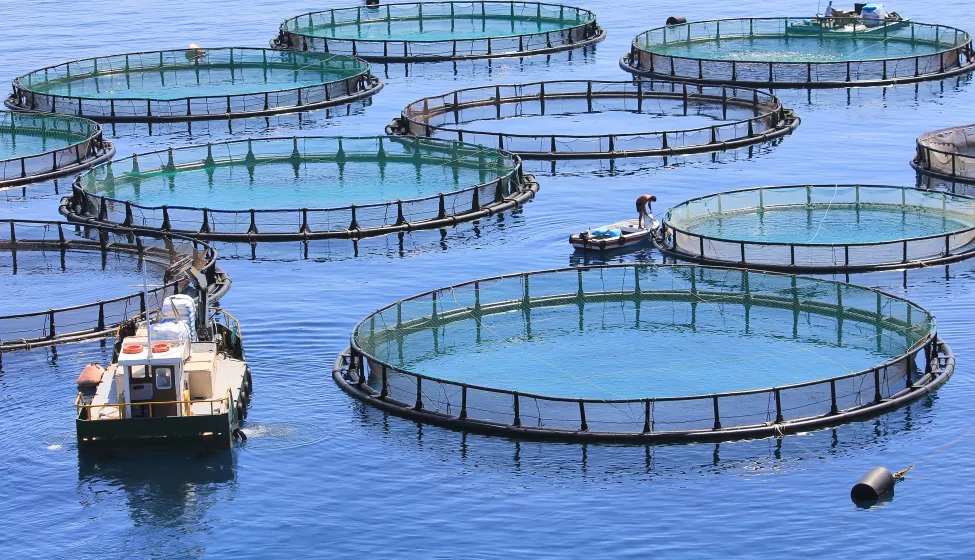
- Aquaculture, underground rivers, oceanariums: for fish and shrimp, aquatic products, aeration or mixing oxygenation
- Wastewater treatment: oxygen-enriched aeration of activated sludge, pool oxygenation
- Ozone generator: provide high concentration of oxygen electrolysis to produce ozone, ozone concentration is higher and more stable, disinfection and bleaching effect is better. Ozone water treatment is basically an oxygen source ozone generator.
How do I Buy an Oxygen Generator?
Purchasing an oxygen generator involves several steps that will guide you to the most suitable equipment for your needs.
Firstly, you need to clearly identify your specific needs. These might be influenced by variables such as the volume of oxygen required, the required purity levels, electricity consumption, geographical location, and local regulations.
For instance, in the healthcare sector, patients’ requirements might depend on their specific health conditions and doctor’s advice, whereas, for industry use, it’s often about the volume and degree of oxygen purity needed for specific processes.
Once you’ve established your requirements, thorough research is pivotal. Begin by selecting reliable suppliers or manufacturers, considering both their reputation and product range. Check customer reviews, get referrals from industry peers, or consult your healthcare provider. Other important factors to consider when choosing a supplier include after-sales service, warranty terms, and availability of spare parts. You should also ensure that the products adhere to international safety and quality standards.
Once you’ve narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed product specifications, pricing, and delivery options. You may want to compare several different models or suppliers to find the most cost-effective solution that meets your needs. Ask about installation, maintenance, and operating costs for an accurate assessment of total cost of ownership.
Finally, before making a purchase, confirm the payment options, shipping, and delivery terms. For large industrial generators, find out if installation assistance is offered. And, especially in the case of healthcare use, it’s essential to understand how to operate the generator safely and efficiently.
In summary, understanding your needs, conducting thorough research, comparing options, and confirming purchase and delivery details are critical steps that will help you make an informed decision when buying an oxygen generator.
Minnuo Professional Oxygen Generator Manufacturer
Minnuo, focusing on improving the quality of oxygen generator, helps to help you realize the gas business and reasonably reduce your operation cost. We have a wide range of oxygen generator plants, such as PSA oxygen generator, cryogenic oxygen generator, VPSA oxygen generator, gas station, etc. If you want to know more, you can directly contact our sales engineers.






 sales2:+86 17506119168
sales2:+86 17506119168

