1 kilogram-force per square centimeter (1 kgf/cm²) is equal to approximately 0.0980665 MPa, which is usually rounded to 0.1 MPa in engineering practice. This simple rule of thumb is widely used when reading gas equipment nameplates, datasheets, and pressure gauges in many countries.
If you often need to convert between kgf/cm², MPa, bar, psi or “kg pressure”, this guide gives you the key formulas, examples and a quick reference table in one place.
In the gas equipment industry, we often encounter questions about pressure unit conversions, such as “How much is 1 kgf/cm² in MPa?” Understanding these conversions is essential for selecting, operating, and maintaining equipment effectively and safely. Here, we’ll provide an in-depth explanation of these common pressure units and how to convert between them.
1 kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm²) is approximately equal to 0.1 MPa. This relationship is widely used in the selection, design, operation, and maintenance of gas equipment. By understanding the conversion between kilogram-force and megapascal, we can more accurately interpret equipment parameters, ensure operational safety, and meet international technical standards.”
Understanding Pressure Units
Pressure is a key parameter in gas equipment and piping systems. Different countries and equipment types sometimes use different units to measure pressure, so understanding these units and how they convert can help you work accurately and efficiently with gas equipment. Here’s a quick overview of the main pressure units commonly used in the gas industry:
Kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm²)
Often referred to simply as “kg/cm²” or “kilogram pressure,” this unit is widely used in the gas industry and various industrial applications. It represents the pressure exerted by a 1-kilogram force on an area of 1 square centimeter. This unit is convenient and easy to understand, making it a popular choice for many traditional applications.
Megapascal (MPa)
MPa is the abbreviation for megapascal, which means one million pascals, or one million newtons of force per square meter. In gas equipment datasheets you will often see values like 0.8 MPa, 1 MPa or 3 MPa, and many users will search “MPa to kg/cm²” or “MPa to kg” when they want to understand these pressures in more familiar units such as kilogram-force per square centimeter.
The megapascal is a widely used unit in modern industry due to its suitability for high pressures and its compatibility with the International System of Units (SI). 1 MPa is equal to one million pascals (Pa), or one million newtons of force per square meter. This unit is widely used in gas equipment and modern industry for its ease of standardization.
The exact relationship between kgf/cm² and MPa is:
- MPa = kgf/cm² × 0.0980665
- kgf/cm² = MPa ÷ 0.0980665
For quick daily use, many engineers remember the rounded rule: - 1 kgf/cm² ≈ 0.1 MPa
- 1 MPa ≈ 10.2 kgf/cm²
This is why searches like “kgf/cm² to MPa”, “MPa to kg/cm²” or “MPa to kgf” are essentially asking for the same conversion between these two pressure units.
Other common units
In addition to kgf/cm² and MPa, other units like the standard atmosphere (atm) and bar are also commonly used. For reference, 1 atmosphere is approximately 0.101325 MPa, and 1 bar is approximately 0.1 MPa. Understanding these units can be helpful when dealing with equipment rated under different standards or for international applications.
So, How Much is 1 kgf/cm² in MPa?
To answer this frequently asked question, let’s look at the conversion relationship between kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm²) and megapascals (MPa):
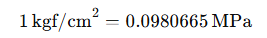
In other words, 1 kilogram-force per square centimeter is approximately equal to 0.0980665 MPa. For ease of calculation, this is often rounded to:
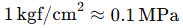
Practical Applications of Pressure Unit Conversion
Understanding the conversion between kgf/cm² and MPa has a wide range of practical applications in the gas industry. Here are some common scenarios where this conversion is especially useful:
Equipment Selection and Design
When selecting or designing equipment, you may encounter specifications using different units. For instance, some older equipment may use kgf/cm², while newer equipment might be rated in MPa. By converting between units, you can accurately compare performance and choose the right model for your needs.
Gas Storage and Piping Systems
Storage tanks and piping systems often need to clearly display their rated pressure in a standard unit. For example, if a tank is rated at 10 kgf/cm², this translates to roughly 0.98 MPa, or about 1 MPa. Converting between units like this helps customers accurately evaluate the pressure performance and understand the tank’s operating conditions.
Operational Maintenance
In operational and maintenance scenarios, understanding the equipment’s pressure parameters is crucial. Technicians familiar with MPa can use the approximate conversion factor of 0.1 MPa for each kgf/cm² to simplify calculations and avoid errors, which can lead to safer and more efficient equipment management.
Pressure Unit Conversion Reference Table
For quick reference, here is a table of common pressure units and their approximate conversions:
Many practical questions such as “1 bar to kg”, “9 bar pressure to kg”, “1 MPa to kg” or “kg to MPa convert” are just different ways to ask for the same relationships shown in this table.
Real-Life Examples of Unit Conversion
To further illustrate the relationship between kgf/cm² and MPa, here are a few practical examples:
Example 1
If a compressor’s outlet pressure is 10 kgf/cm², converting this to MPa gives:
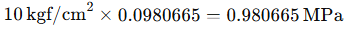
This is approximately equal to 1 MPa.
Example 2
If a gas system’s rated pressure is 5 MPa, converting this to kgf/cm² gives:

These practical examples can help you accurately select, operate, and evaluate equipment for different pressure conditions.
Tips for Using Pressure Conversions Safely and Effectively
To ensure accuracy and safety in daily operations, we recommend keeping the following points in mind when performing unit conversions:
Ensure Consistent Units
When purchasing or operating equipment, make sure that all pressure measurements are in the same unit to avoid data inconsistencies. For example, if an equipment manual uses MPa, ensure all measurements and operations use MPa for clarity and consistency.
Consider Precision
In high-precision gas equipment, even minor conversion errors can affect accuracy and potentially lead to operational risks. For high-pressure equipment, it’s recommended to use exact values for conversions rather than rounded approximations to minimize errors.
Know Your Equipment’s Pressure Range
Different types of equipment have different pressure ranges. For example, low-pressure systems might be better expressed in kilopascals (kPa) or kgf/cm², while high-pressure systems typically use MPa. Choosing the most suitable unit for your equipment can make working with pressure parameters easier.
Quick FAQ: Common Pressure Conversion Questions
Q1: What is 1 kgf/cm² to MPa?
A: 1 kgf/cm² is equal to approximately 0.0980665 MPa, and in most gas applications it is treated as 0.1 MPa for easier mental calculation.
Q2: What is 1 MPa to kgf/cm² (or kg/cm²)?
A: 1 MPa corresponds to about 10.2 kgf/cm², which many technicians simplify to “1 MPa ≈ 10 kg/cm²” when checking pressure ratings or comparing older equipment labels.
Q3: What is the MPa full form?
A: MPa stands for megapascal, a metric unit of pressure equal to one million pascals and widely used in modern gas, hydraulic and mechanical systems.
Q4: How do I convert MPa to kg or kgf?
A: When people search “MPa to kg” they usually mean MPa to kgf/cm²; use the formula kgf/cm² = MPa ÷ 0.0980665 and then interpret kgf as “kilogram-force”, not mass in kilograms.
Q5: How can I convert bar or psi to kgf/cm² or MPa?
A: As a rule of thumb, 1 bar ≈ 0.1 MPa ≈ 1.02 kgf/cm², and 14–15 psi is roughly equal to 1 bar or 1 kgf/cm², which helps when converting “20 psi to kg”, “100 psi to kg” or “150 psi to kg”.
Conclusion
In the gas industry, understanding pressure conversions is not only a routine task but also a key factor in improving safety and operational efficiency. By mastering the conversion between kgf/cm² and MPa, customers can more easily and accurately work with equipment specifications and ensure their equipment’s reliability and compatibility.
Whether it’s selecting the right unit for pressure, confirming equipment parameters, or performing safe operational procedures, a firm grasp of these units and their conversions can help you simplify your daily tasks and improve your equipment’s performance. We hope this guide provides you with a clearer understanding of these pressure units. If you have any further questions or need technical assistance, please feel free to reach out to our support team. MINNUO is here to help!






 sales2:+86 17506119168
sales2:+86 17506119168

