With the improvement of global medical protection level and the growth of industrial safety oxygen demand, oxygen generation equipment has been widely used in hospital ICU, operating room, field rescue station, cold chain processing, metal cutting and other scenarios. Especially in the epidemic prevention and control, emergency response and plateau oxygen replenishment and other unexpected demand frequent background, the user is not only concerned about the purity and flow of oxygen, but also pay more attention to the reliability of the system, deployment efficiency and flexibility of use.So what exactly is the difference between portable and fixed oxygen concentrators?
So, in the actual selection, how should users weigh the “portable” and “stationary” oxygen generation equipment? What is the difference between the two in terms of gas production capacity, mobility, energy allocation, system integration, maintenance difficulties, etc.? What scenarios are they suitable for? This is exactly what this article tries to analyze in depth.
This article will focus on the core dimensions of “gas production capacity, oxygen purity, flexibility, operation and maintenance costs, regulatory compliance” and other comparative analysis of the performance advantages and limitations of the two types of systems, supplemented by typical use scenarios, to help medical, industrial and emergency response users to scientifically select the type, to avoid the waste of resources or the risk of system mismatch.
1. Definition & Working Principles
Before selection, users first need to understand the basic definition, construction differences and technical principles of portable and stationary oxygen generating equipment. This section will clearly explain the system types, core components and typical applications.
1.1 Portable Oxygen Generating Equipment
Portable oxygen generating equipment is a small oxygen generating system designed for flexible deployment and rapid response scenarios, featuring lightweight, integration, low power consumption, etc. It is commonly used in emergency response, mobile medical care and field rescue scenarios.
Common types:
Mobile trolley type: equipped with a wheeled base that can be pushed and used on the go
Vehicle-mounted type: integrated in ambulances, field vehicles and other mobile carriers
Tent supporting system: suitable for temporary isolation zones in the field, campsites and other places with no infrastructure
Core Composition and Technical Characteristics:
Core technology: PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption)
Built-in oil-free air compressor, molecular sieve adsorption module, oxygen storage tanks
Some models can be equipped with battery Some models can be equipped with batteries or used in combination with generators.
Applicable Scenarios:
Temporary oxygen supply for emergency rescue stations or isolated hospitals
Rural health centers, mobile medical teams in infected areas
Non-fixed workplaces, such as plateau clinic rounds and field construction
✅ Advantages Summary: Infrastructure-free deployment, ready to be used after being powered on, suitable for complex environments; however, the gas production capacity and the ability of sustained oxygen supply are relatively limited, which is suitable for the demand of small-flow and short-time oxygen supply.
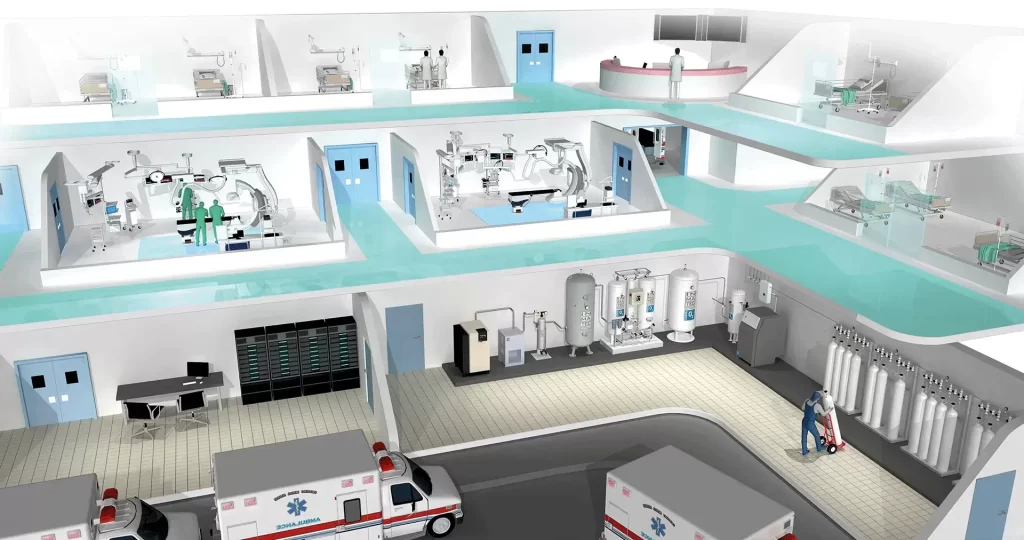
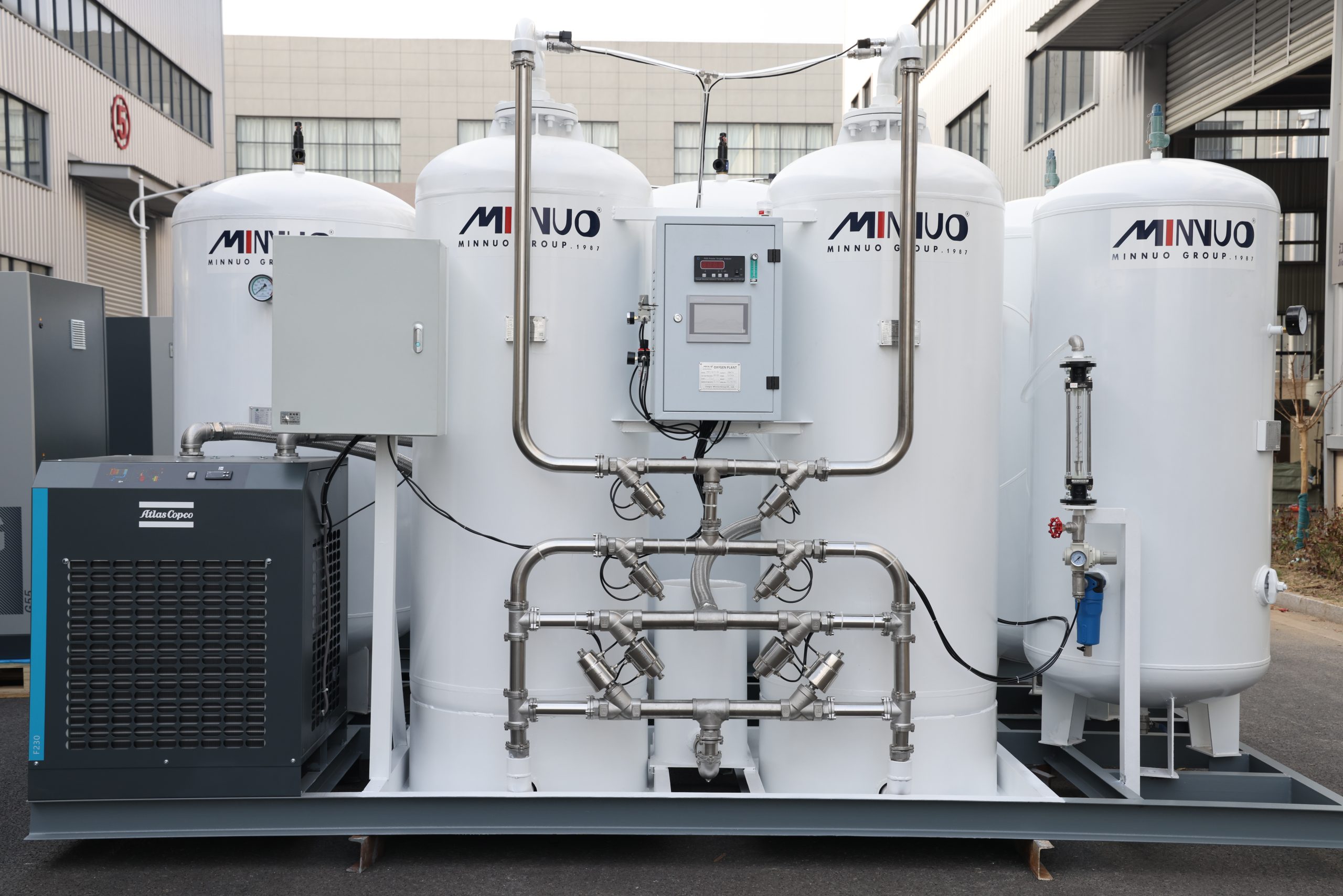
1.2 Fixed Oxygen Plant
Fixed Oxygen Plant is a kind of centralized oxygen plant dedicated to the continuous supply of oxygen in large and medium-sized places, which has stronger system integration capability, higher stability of oxygen supply and degree of automation, and is widely used in high load scenarios such as hospitals, factories and gas stations.
Common types:
Medical centralized oxygen supply system (ICU/operating room)
Industrial oxygen system (welding, glass firing, ozone generation, etc.)
Small oxygen station (serving community hospitals/rehabilitation centers)
Technical features:
Multi-stage PSA module, PLC intelligent linkage control system
Equipped with gas storage tanks, cold dryers, precision filtration systems and other ancillary equipment
Optional automatic water drainage system, alarm modules and remote monitoring interfaces
Applicable scenarios:
Medical institutions: centralized oxygen supply for multiple wards (24h continuous)
Industrial production lines: oxygen source for oxygen welding and cutting, ozone system
Schools/nursing homes/laboratories and other areas that need oxygen but do not have a bottled supply chain
✅ Advantages Summary: Stable output, intelligent inter-control, support for multi-point oxygen delivery; however, the installation cycle is long, occupies a large area, and requires a good power supply and civil engineering foundation.
2. Comparison Criteria
When choosing portable or stationary oxygen production equipment, enterprises or organizations should take into account their own needs and make a comprehensive evaluation in six key dimensions, including gas production capacity, oxygen purity, ease of deployment, energy suitability, maintenance cost and budget investment.
2.1 Oxygen Production Capacity
Portable system: Usually low-flow oxygen supply in L/min, suitable for single-person or temporary small-scale use, such as at the emergency bedside, in remote villages or in the field.
Fixed system: measured in Nm³/h (standard square per hour), supporting high flow, multi-terminal oxygen delivery, able to meet the demand of continuous gas supply for 24 hours in multiple hospital wards or industrial sections.
✅ Application judgment: If there is a long-term operation demand or multiple gas consumption points, it is recommended to choose fixed system as a priority.
2.2 Oxygen Purity
Portable equipment: most of the output is 93%±3% medical oxygen, which has already complied with the medical standard YY/T 0298 and is suitable for basic treatment and routine oxygen use scenarios.
Stationary equipment: support three-stage purification module, can output 93%, 95% and industrial grade 99.5% or more oxygen, to meet the high purity process scenarios such as glass firing, ozone reaction and so on.
✅ Applicable judgment: High-end process, export-oriented enterprises, pharmaceutical/food-grade oxygen is recommended to use fixed type.
2.3 Mobility and Installation
Portable equipment: high integration, one person can push or get on the car, deployment only needs to be powered on, suitable for unexpected emergency and flexible site switching.
Fixed system: need to consider site selection, water, electricity and gas supporting construction, construction cycle ranging from 2 to 6 weeks, need to be installed and commissioned by a professional engineering team.
✅ Applicable judgment: temporary deployment or mobile scenarios (such as disaster areas/field/vehicle) choose portable more advantageous.
2.4 Energy Consumption & Power Supply
Portable system: low power, suitable for generator or battery car power supply, but slightly higher energy consumption per unit of oxygen production due to flow restrictions.
Fixed system: Despite the higher initial power, it supports energy efficiency optimization strategies such as frequency conversion energy saving, night standby, zoned oxygen supply, etc., and the overall energy consumption/oxygen production ratio is better.
✅ Application judgment: focusing on long-term energy consumption, nighttime operation or the need to configure photovoltaic standby energy, it is recommended to choose the fixed type.
2.5 Reliability and Maintenance
Portable equipment: simple structure, easy to maintain, suitable for grass-roots units, but the life span is relatively short (2~5 years), and key components such as molecular sieve consumables are replaced frequently.
Fixed system: high system integration, high stability, usually can realize ≥720 hours of continuous operation without interruption, but need regular maintenance, replacement of filters, oil separators, etc.
✅ Applicable judgment: If the working condition requires high stability and less failure, fixed oxygen equipment is more suitable.
2.6 Cost Analysis
| Cost Dimension | Portable Oxygen Plant | Fixed Oxygen Plant |
| Initial Investment | Low ($10,000~$50,000) | High ($100,000~300,000) |
| Unit Operating Costs | Slightly high (centralized energy consumption, manual changeover) | Low (automatic system control) |
| O&M Costs | Frequent molecular sieve replacement | High cost of long-cycle spare parts |
| Life Cycle Benefits | Suitable for emergency or temporary projects | More suitable for long-term stabilization scenarios |
Conclusion Recommendation: Portable is suitable for low-budget, short-term needs; stationary is suitable for total cost control and the pursuit of continuous oxygen supply scenarios.
Use Case Scenario
| Scenario Categories | Recommended Equipment Types | Reasons |
| Field Medical Rescue | Portable Oxygen Equipment | Rapid deployment, low power consumption, self-storage of oxygen |
| Centralized Oxygen Supply for ICU Ward | Stationary Oxygen Systems | High flow rate, stable oxygen supply, easy to centralize control |
| Vehicular or Remote Site | Portable (Truck Mounted) Systems | High mobility, can be linked with generators |
| Oxygen for Large-Scale Factories | Stationary + Tank Systems | High usage, can be connected to the grid, can be intelligently linked with PLC system control |
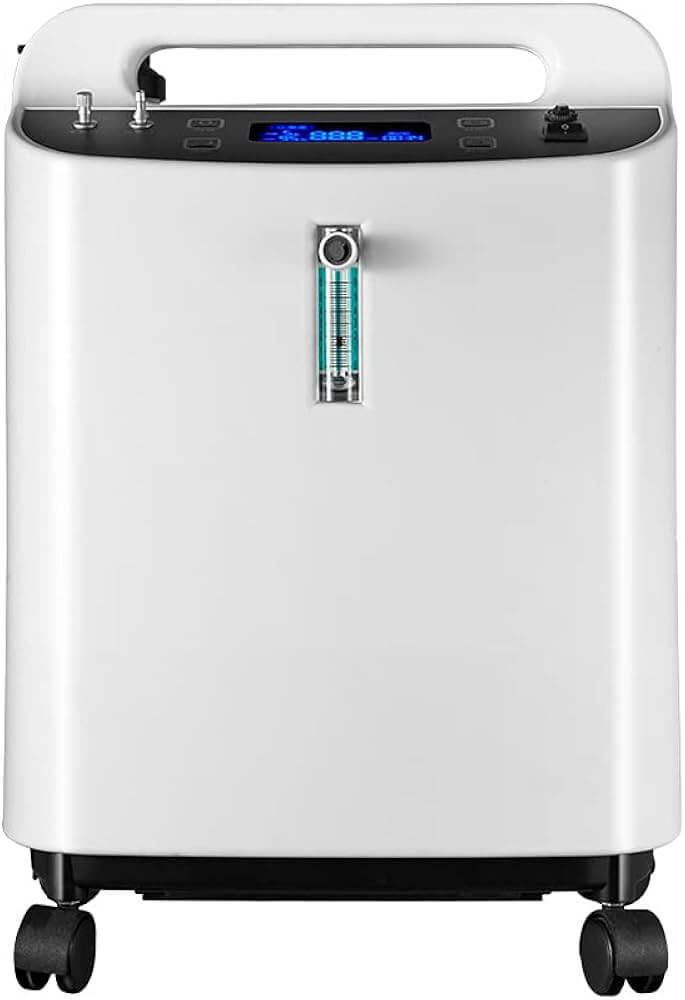
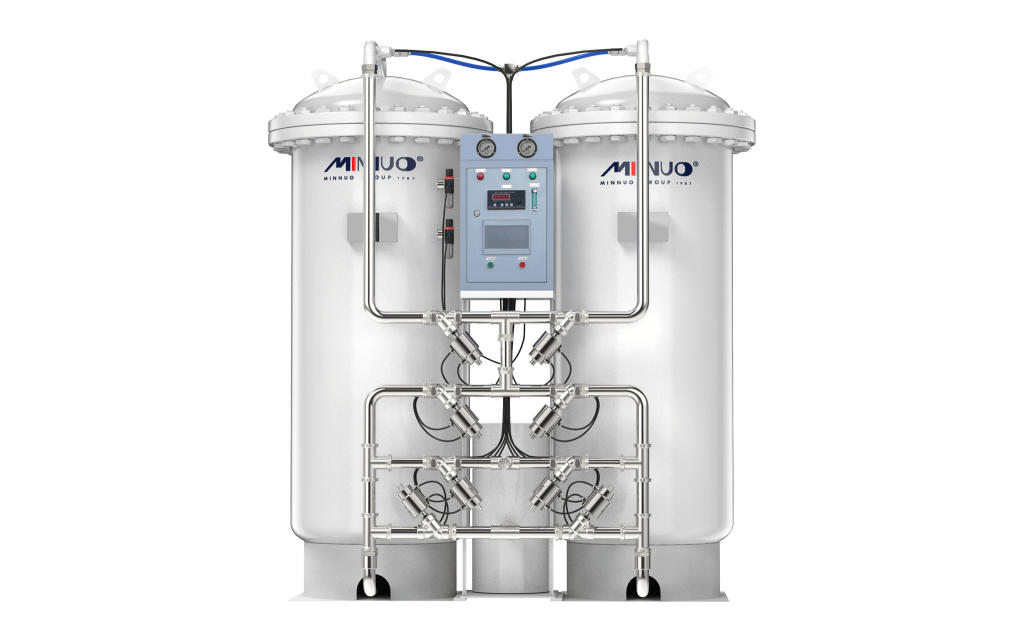


3. Integration & Flexibility
Under different usage scenarios, the scalability and compatibility of the oxygen generation system directly determines the efficiency of subsequent operation and maintenance, the level of informationization management and the ability to adapt to multiple scenarios. Portable and fixed systems have their own advantages in integration, linkage, remote control, etc. Enterprises should select the system flexibly according to the deployment environment and development expectations.
3.1 Integration and Expansion Capability of Fixed Oxygen Generation System
Centralized Oxygen Supply Pipeline Network Docking: It can be used as the central oxygen supply station in hospitals or factories, and supports multi-point, multi-floor and multi-terminal pipeline oxygen supply layout.
Support remote monitoring and PLC linkage: real-time data can be uploaded through Ethernet, serial port or cloud, and support linkage with upper computer, SCADA and MES system to realize intelligent management of gas source system.
Data collection and traceability: Equipped with oxygen concentration, flow rate and pressure monitoring module, it realizes 24-hour online record, over-limit alarm and history traceability, which meets the needs of compliance scenarios such as medical, pharmaceutical, food and so on.
Supports compatibility with UPS or diesel generator: Ensures continuous oxygen supply in power failure scenarios, suitable for high-reliability industries (e.g. ICU, ICU ward, welding section).
✅ Application suggestion: If you need to integrate with the existing plant/hospital network, or consider the future intelligent management upgrade, you should give priority to the fixed oxygen generation equipment with standardized communication interface and centralized management function.
3.2 Flexible compatibility of portable oxygen system
Flexible combination with oxygen storage system: support external storage cylinders, airbag packages and portable buffer tanks to realize short-time offline oxygen supply or mobile delivery in unexpected scenarios.
Adaptable to shunt valve and multi-user terminal: with multi-output valve, it can supply oxygen independently to multiple patients/equipment, which is suitable for disaster scene, mobile diagnostic and treatment vehicle and other small-volume multi-point gas supply scenarios.
Embedded power supply and vehicle linkage: It can be connected to vehicle power supply (12V/24V) or portable battery pack to realize cooperative operation in ambulance, transfer vehicle, field station and other mobile medical systems.
Strong environmental compatibility: Some models support -10°C~+45°C wide temperature band operation, suitable for plateau, desert, humidity and other variable climate conditions.
✅ Application suggestions: Portable systems are preferred for emergency rescue, vehicle deployment, and remote area medical rounds; application flexibility can be expanded through the “mainframe+accessory combination” approach.

4. Regulatory & Safety Considerations
When choosing portable or stationary oxygen generating equipment, regulatory certification and safety are the core indicators that cannot be ignored, especially when it comes to highly sensitive application scenarios such as medical care, rescue, emergency response, welding, etc.
4.1 Comparison of regulatory approvals: whether they meet the requirements for market entry and use in different scenarios.
| Type | Common Certification Requirements | Is it mandatory | Description of Application |
| CE (EU) | EU Medical Device Regulation MDR 2017/745, EMC Directive, LVD Directive | Yes | All medical devices exported to the EU |
| ISO13485 | Medical Device Quality Management System Certification | Medical recommendation | Medical Scenario Compliance, Documentation Traceability |
| FDA 510(k) | U.S. Food and Drug Administration Certification | Yes (medical) | Required for the North American market, with stringent documentation requirements |
| YY/T 0298, GB 9706 Series | China Medical Device Strong Standard | Yes | Procurement by domestic hospitals and emergency units |
Suggestion: Fixed systems used in medical scenarios must obtain ISO13485 and CE certificates; portable devices should also have CE, EMC and other compliance reports when exported.
4.2 Structural and Electrical Safety Standards
Electrical Safety: Whether it complies with IEC 60601, GB 9706.1 and other safety standards for electrical medical devices to ensure overload protection, short-circuit prevention and leakage prevention.
Oxygen leakage prevention and control design: Stationary oxygen stations should be equipped with flow sensors, oxygen concentration monitoring module, and support abnormal power failure/pressure offset alarm.
Anti-misoperation protection: Portable equipment is recommended to be equipped with “anti-reverse flow valve for misconnection of gas source”, “battery power alert” and “one-key low oxygen alarm” module.
4.3 Environmental adaptability: the stability and reliability of the equipment in special use environment.
| Environmental Adaptation Dimensions | Stationary Oxygen Systems | Portable Oxygen Generation System |
| Vibration Resistance | Typically requires seismic base/wall bracket installation | Compact internal structure with vibration-resistant support system |
| Dust and Moisture Resistance | Equipped with dust cover and ventilated heat exchanger | Enclosed, suitable for outdoor/emergency hot and humid environments |
| Operating Temperature and Humidity Range | Typically 5°C~80% RH | Wide temperature (-10~+45°C) adaptability |
| High Plains Adaptation | Optional High Plains Air Compressor Module Available | Lightweight and easy to pressurize, can reach more than 3,000m of normal oxygen supply |
Suggestion: If used in mobile diagnostic and treatment vehicles, field station, plateau or high-temperature environments, you should prioritize equipment with IPX4 or higher level of protection and pass the temperature and humidity endurance test of the whole machine.
4.4 Differences in safety compliance between medical grade vs. industrial grade equipment
| Safety Dimensions | Medical grade equipment (e.g. ICU oxygen supply) | Industrial equipment (e.g. welding/cutting) |
| Oxygen Concentration Monitoring | Online monitoring with upper/lower limit alarms | Optional, only for some high-end models |
| Flow Output Control | Accurate (L/min level), recordable and traceable | Mostly Nm³/h measurement, no data traceability |
| Usage Interfaces | Medical humidification bottle/nasal oxygen tube interface | Universal joints/welding gas joints predominantly |
| Regulatory Enforcement Body | State Drug Administration + Health System | MIIT + Safety Supervision System |
❓ FAQ
Q1: How to judge whether I am suitable for portable or fixed oxygen system?
A: You can judge from three aspects: ① Usage scenarios: portable is preferred for emergency and mobile places; fixed is preferred for hospital ICUs, factories and other continuous oxygen supply places; ② Oxygen production demand: portable is recommended for less than 10 L/min and fixed is recommended for more than 10 L/min; ③ Installation conditions: portable is recommended if you can’t connect to the power supply or lack of installation basis.
Q2: Does portable oxygen equipment support medical grade oxygen (≥93%)?
A: Some of the high-end portable equipment (such as MINNUO portable medical series) adopts PSA oxygen technology, equipped with precision sensors, output oxygen purity ≥93%, which can meet the needs of mobile medical vehicles, first aid units and so on.
Q3: Can stationary oxygen system supply multiple wards or workstations at the same time?
A: Yes, the stationary equipment supports centralized oxygen supply and zoned air supply design, and can achieve plant/ward-wide coverage through multi-point gas distribution pipe network + flow adjustment module, which is suitable for large-scale medical institutions and industrial oxygen centers.
Q4: How to control system operation cost? Which one is more energy efficient?
A: Fixed system is more energy-efficient for long-term operation, especially MINNUO’s intelligent energy-saving control system supports night-time low-power mode and load adaptive adjustment, which significantly reduces the annual operating cost compared with frequent replacement of gas cylinders or liquid oxygen refill.
Q5: Does MINNUO provide customized solutions? Can it support remote management?
A: Yes, MINNUO provides modular + customized oxygen generation system, including PLC remote monitoring, automatic oxygen concentration alarm, cloud data collection, etc., which supports the whole process of intelligent integration from front-end oxygen supply to back-end management.
Conclusion
Portable and stationary oxygen generators have their own advantages: the former is suitable for flexible deployment scenarios such as field medical care, emergency vehicles, mobile clinics, etc., emphasizing ready-to-use and lightweight integration; the latter, with its high flow rate, high purity, and stable control capability, is more suitable for hospital ICUs, industrial production lines, and other environments with high requirements for oxygen supply continuity and system scalability.
MINNUO provides customized oxygen solutions covering both types of needs, supporting centralized oxygen supply, remote monitoring, intelligent linkage and modular deployment, helping customers to efficiently match scenarios, reduce usage costs, and build a safer and more compliant oxygen protection system.






 sales2:+86 17506119168
sales2:+86 17506119168

