In the industrial sector, nitrogen is widely used in industries such as chemicals, electronics, food, and pharmaceuticals due to its inertness, non-corrosiveness, and stable chemical properties. Currently, cryogenic air separation, pressure swing adsorption (PSA), and membrane separation are the mainstream nitrogen generation methods. This article will provide an in-depth and professional comparison of these three technologies from multiple dimensions, including principles, characteristics, and applicable scenarios.
Cryogenic air separation, PSA, and membrane separation are the three mainstream nitrogen generation technologies in the industry. Cryogenic air separation is suitable for large-flow, high-purity nitrogen demands, with complex equipment and high energy consumption, making it ideal for industries such as petrochemicals and steel. PSA technology, on the other hand, offers fast startup and low costs, making it suitable for small to medium-scale applications, especially in fields like electronics manufacturing and food preservation. Membrane separation nitrogen generation is known for its fast response and simple structure, making it suitable for industries with lower purity requirements, such as oilfield nitrogen injection and laser cutting.
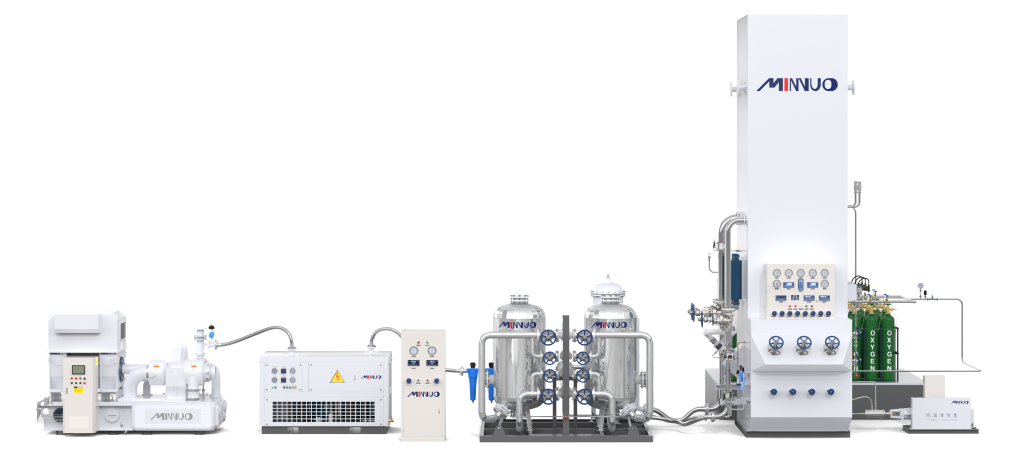
I. Cryogenic Air Separation Nitrogen Generation
(1) Principle and Process
Cryogenic air separation, a traditional and classic process, has been developed for decades. Its core principle is based on the significant differences in the boiling points of air components, achieving air separation through deep freezing. The specific process is as follows:
- Air Compression: Ambient air first enters an air compressor, where the pressure is increased to 0.6 – 0.8MPa. This process not only provides power for subsequent purification and cooling but also makes the air’s physical properties easier to handle.
- Air Purification: The compressed air contains impurities such as moisture, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons. If not removed, these impurities can freeze or block pipelines during the low-temperature process, affecting normal equipment operation. Therefore, the compressed air is purified through an air precooling system and a molecular sieve purification system. In the air precooling system, the compressed air is cooled to 10 – 15°C using chilled or circulating water, causing most of the water vapor to condense and separate. The molecular sieve purification system uses specialized adsorbents to further remove residual moisture, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons, ensuring the purified air has a dew point below -65°C and a carbon dioxide content below 1×10⁻⁶.
- Air Liquefaction: The purified air enters the main heat exchanger, where it is gradually cooled to near the liquefaction temperature (approximately -196°C) through heat exchange with returning low-temperature gas. It then passes through a throttle valve, where the pressure is reduced, further cooling and liquefying the air to form liquid air.
- Distillation Separation: The liquid air enters a distillation column, typically consisting of an upper and lower column. In the lower column, the liquid air undergoes preliminary distillation under a certain pressure. Since oxygen has a higher boiling point (-183°C) than nitrogen (-196°C), oxygen gradually accumulates at the bottom of the column, forming oxygen-rich liquid air, while nitrogen escapes as a gas at the top. Part of the nitrogen is condensed and collected as liquid nitrogen, while the rest is returned to the lower column as reflux to ensure mass and heat transfer during distillation. The oxygen-rich liquid air is then throttled into the upper column for further distillation, ultimately producing high-purity nitrogen (up to 99.999%) at the top and high-purity liquid oxygen at the bottom.
(2) Technical Characteristics
- High Purity and Large Capacity: Cryogenic air separation can stably produce ultra-high-purity nitrogen, typically reaching 99.999% or higher. In some advanced systems, nitrogen purity can reach 99.9999%. In terms of capacity, large cryogenic air separation systems can produce thousands to tens of thousands of Nm³/h. For example, a large steel company uses a cryogenic air separation system with a single-unit capacity of 50,000 Nm³/h, fully meeting the demand for high-purity, large-flow nitrogen in large-scale industrial production.
- Complex Equipment: Cryogenic air separation systems are large and complex, requiring key equipment such as large air compressors, air precooling systems, molecular sieve purification systems, main heat exchangers, and distillation columns. The entire system occupies a large area. For example, a cryogenic air separation system with a capacity of 10,000 Nm³/h typically requires 2,000 – 3,000 square meters. The construction cost is high, not only due to the expensive equipment but also the complex installation and commissioning process, which usually takes 1 – 2 years.
- Operating Costs and Startup Time: Cryogenic air separation nitrogen generators have high energy consumption, primarily due to the need for air compression and low-temperature refrigeration, which require significant electrical power. Statistics show that producing 1 Nm³ of nitrogen with 99.999% purity consumes approximately 0.6–0.8 kWh of electricity.The startup time exceeds 6 hours because the system must gradually cool down to low temperatures and establish stable rectification conditions. This process involves multiple stages, including preheating, precooling, and commissioning. Any issues during these stages can prolong the startup time. Therefore, cryogenic air separation nitrogen generators are best suited for continuous, stable operation in large-scale industrial applications, as frequent startups and shutdowns significantly increase operational costs and equipment wear.
- Small Cryogenic Air Separation Units: Models such as the KZO-120 oxygen generator, with a flow rate of 120 Nm³/h, typically require 6–8 hours for startup.
- Medium Cryogenic Air Separation Units: Common 6000 Nm³/h air separation units usually take over 10 hours to start. With optimized operation, the startup time can be reduced by approximately 3 hours.
- Large Cryogenic Air Separation Units: Systems with capacities of 35,000 Nm³/h or more have a more complex startup process, requiring 24 hours or longer to complete.
- Economic Efficiency: For nitrogen demands below 3,500 Nm³/h, the investment cost of cryogenic air separation is 20% – 50% higher than that of PSA. This is due to the complexity and large scale of cryogenic air separation systems, resulting in higher equipment procurement, installation, commissioning, and maintenance costs. However, for large-scale nitrogen demands (above 3,500 Nm³/h), the unit cost decreases as production increases, demonstrating economies of scale and making it more suitable for ultra-large-scale nitrogen demands.
(3) Applicable Scenarios
Cryogenic air separation is suitable for industries such as petrochemicals, steel metallurgy, and coal chemicals that require high-purity, large-flow nitrogen. In the petrochemical industry, nitrogen is often used as a protective, purging, and sweeping gas in processes like hydrocracking and catalytic reforming, requiring high purity and stable flow. In the steel industry, high-purity nitrogen is used in processes like converter steelmaking and continuous casting for cooling oxygen lances and protecting molten steel, with stringent requirements for nitrogen purity and flow. For example, a large petrochemical company uses a cryogenic air separation system to provide nitrogen with a purity of 99.999% and a flow rate of 8,000 Nm³/h, ensuring the safe and stable operation of its hydrocracking process.

II. PSA Pressure Swing Adsorption Nitrogen Generation
(1) Principle and Process
PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) nitrogen generation technology emerged in the 1970s and is a gas separation technology based on the differential adsorption characteristics of adsorbents for different gases. Its core principle is the selective adsorption of oxygen and nitrogen by carbon molecular sieves. The specific process is as follows:
- Air Compression: Ambient air is compressed to 0.7 – 0.8 MPa by an air compressor, providing the necessary pressure for subsequent adsorption separation.
- Air Purification: The compressed air contains moisture, oil, and impurities, which are removed by an air filter to eliminate most liquid water and solid particles. The air is then passed through a refrigerated dryer to reduce the dew point to 2 – 10°C, further removing moisture to ensure the normal operation of the adsorption process.
- Adsorption Separation: The purified air enters an adsorption tower filled with carbon molecular sieve adsorbent. Under pressure (typically 0.7 – 0.8 MPa), the carbon molecular sieve preferentially adsorbs oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor, while nitrogen passes through the adsorption bed and is collected as product gas. When the carbon molecular sieve reaches saturation, the pressure in the adsorption tower is reduced (typically to atmospheric pressure), allowing the adsorbed oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor to desorb, regenerating the adsorbent. By alternating the operation of multiple adsorption towers, continuous nitrogen production is achieved.
(2) Technical Characteristics
- Flexibility and Convenience: PSA nitrogen generation systems have a short startup time, typically requiring only 15 – 30 minutes to reach stable nitrogen production, allowing for quick response to changes in production demand. Nitrogen purity can be flexibly adjusted between 95% – 99.999% by modifying parameters such as adsorption time and pressure, meeting different user requirements. The equipment has a high degree of automation, using advanced programmable logic controller (PLC) systems for remote monitoring and automatic adjustment, significantly reducing manual operation and labor costs.
- Cost Advantage: The equipment is compact, with a small footprint. For example, a PSA system with a capacity of 1,000 Nm³/h typically occupies 50 – 100 square meters. The investment cost is lower than that of cryogenic air separation systems, primarily due to the simpler equipment, which does not require complex low-temperature refrigeration systems or large distillation columns. In terms of operating costs, since it does not consume large amounts of electricity for refrigeration, the energy consumption is relatively low, with approximately 0.3 – 0.5 kWh required to produce 1 Nm³ of 99% pure nitrogen. PSA systems are particularly suitable for small to medium-scale demands (200 – 3,000 Nm³/h), where they offer significant cost-performance advantages.
- Easy Maintenance: PSA systems do not have low-temperature equipment, with the main components being adsorption towers, air compressors, and air purification equipment. The equipment structure and working principles are relatively simple. The carbon molecular sieve adsorbent typically has a lifespan of 5 – 8 years, during which only regular maintenance of air filters and dryers is required, along with the replacement of wear parts. Maintenance frequency is low, and ordinary technicians can operate and maintain the system after simple training.
- Energy Consumption: Compared to cryogenic technology, PSA systems have lower energy consumption. However, it should be noted that when nitrogen purity exceeds 99.9%, longer adsorption times or additional adsorption towers are required to maintain high purity, leading to a significant increase in energy consumption. For example, increasing nitrogen purity from 99% to 99.99% may increase energy consumption by 30% – 50%.
(3) Applicable Scenarios
PSA nitrogen generation technology is suitable for industries such as electronic component manufacturing, food preservation, and pharmaceutical packaging, where small to medium-scale nitrogen demands with varying purity requirements exist. In the electronics industry, high-purity nitrogen is used to purge and protect chips during manufacturing, preventing oxidation or contamination. Depending on the process, nitrogen purity can range from 99.9% – 99.999%. In the food industry, nitrogen is used to displace oxygen in food packaging, extending shelf life, with typical purity requirements of 95% – 99%. In the pharmaceutical industry, nitrogen is used as a protective gas in drug packaging to prevent oxidation, with flexible purity requirements. For example, an electronic chip manufacturer uses a PSA system to provide nitrogen with a purity of 99.99% – 99.999%, meeting the production requirements for nitrogen purity and flow.
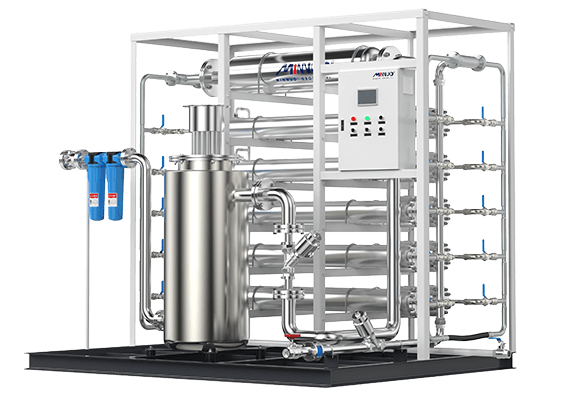
III. Membrane Separation Nitrogen Generation
(1) Principle and Process
Membrane separation nitrogen generation is a novel gas separation technology based on the differential permeation rates of gas components through polymer membranes. The principle involves using specialized polymer membrane materials that selectively permeate different gases. Oxygen, water vapor, and other “fast gases” permeate the membrane faster than nitrogen, leaving a nitrogen-enriched gas stream. The specific process is as follows:
- Air Compression: Ambient air is compressed to 0.7 – 1.0 MPa by an air compressor, increasing the air pressure to provide the driving force for gas permeation through the membrane module.
- Air Purification: The compressed air undergoes purification to remove dust, impurities, and liquid water through an air filter, followed by an activated carbon filter to remove odors and residual oil, ensuring clean air enters the membrane module and preventing contamination or clogging.
- Membrane Separation: The purified air enters the membrane module, which consists of thousands of hollow fiber membranes, each with an inner diameter of 0.05 – 0.2 mm. When air enters the membrane module under pressure, oxygen, water vapor, and other “fast gases” permeate the membrane quickly due to their smaller molecular size and higher diffusion coefficient, while nitrogen is largely retained, resulting in a nitrogen-enriched gas stream at the outlet. By adjusting the number of membrane modules and operating pressure, nitrogen purity and flow can be controlled.
(2) Technical Characteristics
- Rapid Response: Membrane separation nitrogen generation systems have a startup time of only about 3 minutes, enabling almost instantaneous nitrogen supply. This rapid response capability makes them particularly suitable for scenarios requiring frequent startups or emergency nitrogen supply, such as oilfield nitrogen injection, where temporary increases in nitrogen demand or emergency situations require quick nitrogen supply.
- Simple Structure: Membrane separation systems do not have valve switching or complex control systems, consisting mainly of an air compressor, air purification equipment, and membrane modules. The equipment is compact, with a small footprint. For example, a membrane separation system with a capacity of 50 Nm³/h typically occupies 10 – 20 square meters, making it easy to install and move. Maintenance costs are very low, with membrane modules typically lasting 3 – 5 years, requiring only regular maintenance of air filters and activated carbon filters, without the need for specialized technicians.
- Purity Limitations: The economic purity range for membrane separation nitrogen generation is 95% – 98%. If nitrogen purity above 99% is required, multi-stage membrane separation or a combination with other technologies is needed, significantly increasing equipment costs by more than 15% compared to PSA systems. This is because higher nitrogen purity requires more membrane modules and higher performance(A single membrane module from brands such as Air Products and Generon can achieve 99.5%), along with additional auxiliary equipment for finer gas separation.
- Scalability: Membrane separation systems can be quickly expanded by adding membrane modules in parallel. As production demands change, increasing the number of membrane modules can easily increase system capacity. This scalability makes them suitable for dynamic demand scenarios, such as small laboratories where nitrogen demand increases with additional experiments, allowing for easy system expansion by adding membrane modules.
(3) Applicable Scenarios
Membrane separation nitrogen generation is suitable for oilfield nitrogen injection, laser cutting, small laboratories, and other fields requiring medium purity (≤98%) and rapid nitrogen supply. In oilfield nitrogen injection, nitrogen is used to enhance oil recovery, with typical purity requirements of 95% – 98%. Membrane separation systems can quickly respond to nitrogen injection demands, providing the required nitrogen in a timely manner. In laser cutting, nitrogen is used as an auxiliary gas to remove slag and prevent oxidation during cutting, with typical purity requirements around 95%. The rapid nitrogen supply and low cost of membrane separation systems make them widely used in this field. In small laboratories, where nitrogen demand is low but rapid nitrogen supply is required, membrane separation systems are ideal. For example, an oilfield uses a membrane separation system to provide nitrogen with a purity of 97% for nitrogen injection, with the system able to start and operate stably in a short time, meeting the oilfield’s rapid nitrogen supply needs.

IV. Comprehensive Comparison and Selection Recommendations
| Parameter | Cryogenic Air Separation (Nitrogen) | PSA Nitrogen Generation | Membrane Separation Nitrogen Generation |
| Nitrogen Purity | Above 99.999% | 95% – 99.999% | 95% – 98% |
| Startup Time | 12 – 24 hours | 15 – 30 minutes | 3 minutes |
| Production Capacity | Large-scale (>3000 Nm³/h) (a minimum of 50 Nm³/h can also be manufactured) | Small to medium scale (200–3000 Nm³/h) (capable of meeting demands from 1 to 3000 Nm³/h) | Small-scale (<200 Nm³/h) (can be manufactured from 1 Nm³/h to 5000 Nm³/h) |
| Investment Cost | High | Medium | Low (when purity ≤ 98%) |
| Operating Cost | High (high energy consumption) | Low (energy consumption increases when purity >99.9%) | Medium |
| Equipment Complexity | Complex, includes large compressors, refrigeration, and distillation equipment | Relatively simple, mainly adsorption towers and purification equipment | Simple, mainly membrane modules and purification equipment |
| Maintenance Difficulty | High, requires professional technicians for cryogenic equipment | Low, can be maintained by ordinary technicians | Extremely low, simple maintenance of membrane modules and purification equipment |
| Applicable Scenarios | Heavy industries such as steel and chemicals with high purity and flow requirements | Industries like electronics, food, and pharmaceuticals, requiring medium-scale production with diverse purity needs | Fields like oilfields, laser cutting, small laboratories, where moderate purity is required and quick nitrogen supply is needed |
Selection Recommendations
- Ultra-large-scale high-purity demand: When a company’s nitrogen demand exceeds 3,500 Nm³/h and requires extremely high purity (99.999% or higher), cryogenic air separation is the preferred choice. Although the investment and operating costs are high, the unit cost is advantageous in large-scale production, and it can stably provide high-purity nitrogen, meeting the production needs of heavy industries like steel and chemicals.
- Small to medium-scale flexible demand: For nitrogen demands between 5 – 3,000 Nm³/h with flexible purity requirements ranging from 95% – 99.999%, PSA offers the best cost-performance ratio. Its short startup time, low equipment cost, and easy operation and maintenance make it well-suited for industries like electronics, food, and pharmaceuticals.
- Rapid response and medium purity: If a company requires rapid nitrogen supply with medium purity (95% – 98%), such as in oilfield nitrogen injection, laser cutting, or small laboratories, membrane separation is the ideal choice. However, it is important to note its purity limitations. When purity requirements exceed 99.5%, other nitrogen generation technologies should be considered based on cost and technical feasibility.
V.MINNUO Advantages
As a professional manufacturer with years of experience in the industrial nitrogen generation field, MINNUO is committed to technological innovation, providing efficient, reliable, and intelligent nitrogen generation solutions tailored to the unique needs of different industries. With deep expertise in the development and optimization of the three major nitrogen generation technologies, MINNUO demonstrates significant advantages in technical adaptability, system energy efficiency, and full lifecycle services. Based on a deep understanding of vertical industries, MINNUO has developed industry-specific nitrogen generation systems:
- Electronics-grade ultra-high-purity nitrogen: Using three-stage catalytic purification and low-temperature adsorption technology, hydrocarbon impurities are controlled below 0.1 ppb, meeting the requirements for chip manufacturing below 28 nm.
- Food and pharmaceutical-grade sterile nitrogen: Integrated with hydrogen peroxide sterilization modules and online particle monitoring (0.01 μm resolution), compliant with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 regulations.
- Oilfield nitrogen injection enhancement system: Developed with anti-pulsation membrane separation technology, output pressure fluctuations are ≤±1%, combined with downhole temperature and pressure sensors for precise closed-loop control of nitrogen injection.
VI. Conclusion
Cryogenic air separation, PSA, and membrane separation nitrogen generation technologies each have unique advantages and applicable scenarios, playing important roles in different industrial fields and complementing each other. When selecting a nitrogen generation technology, companies must comprehensively consider factors such as nitrogen purity, capacity, investment cost, operating cost, maintenance difficulty, and dynamic demand.
If you have any questions, feel free to consult MINNUO!






 sales2:+86 17506119168
sales2:+86 17506119168

