I. Introduction: Why Nitrogen Generator Maintenance Matters
Nitrogen generators are critical equipment in industrial sectors like manufacturing, food packaging, electronics, oil & gas, and pharmaceuticals—providing high-purity nitrogen for processes ranging from inerting and purging to product preservation.
Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced nitrogen purity (compromising product quality), increased energy consumption, unplanned downtime, and costly repairs. Regular, targeted maintenance ensures consistent performance, extends equipment lifespan (typically 10–15 years with proper care), and maximizes return on investment. This guide covers actionable maintenance practices, troubleshooting, and schedules tailored to industrial nitrogen generator systems.
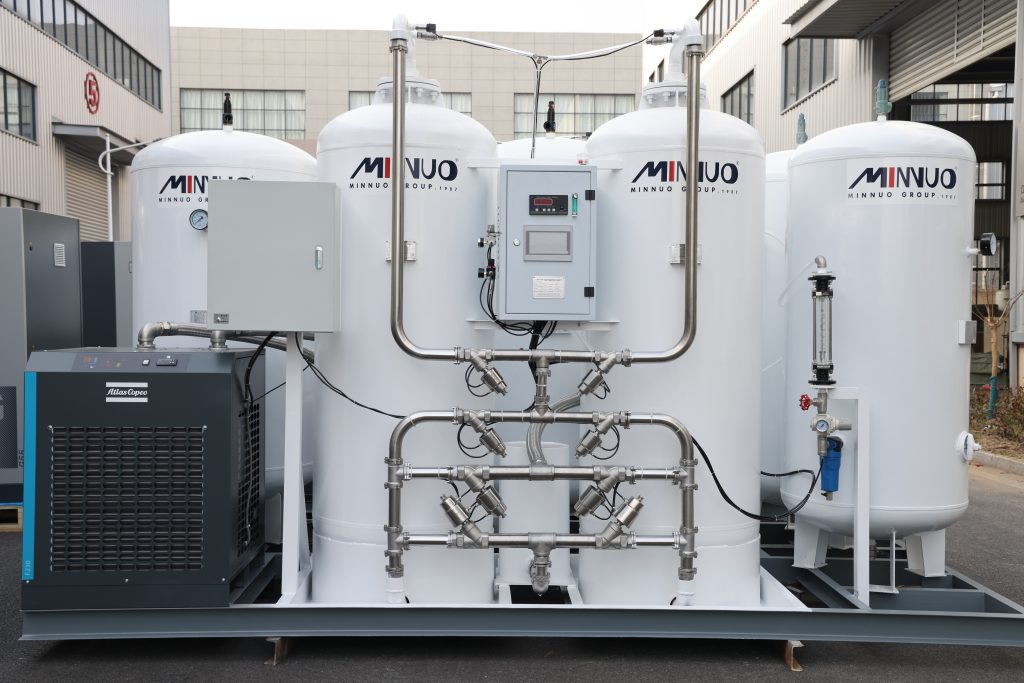

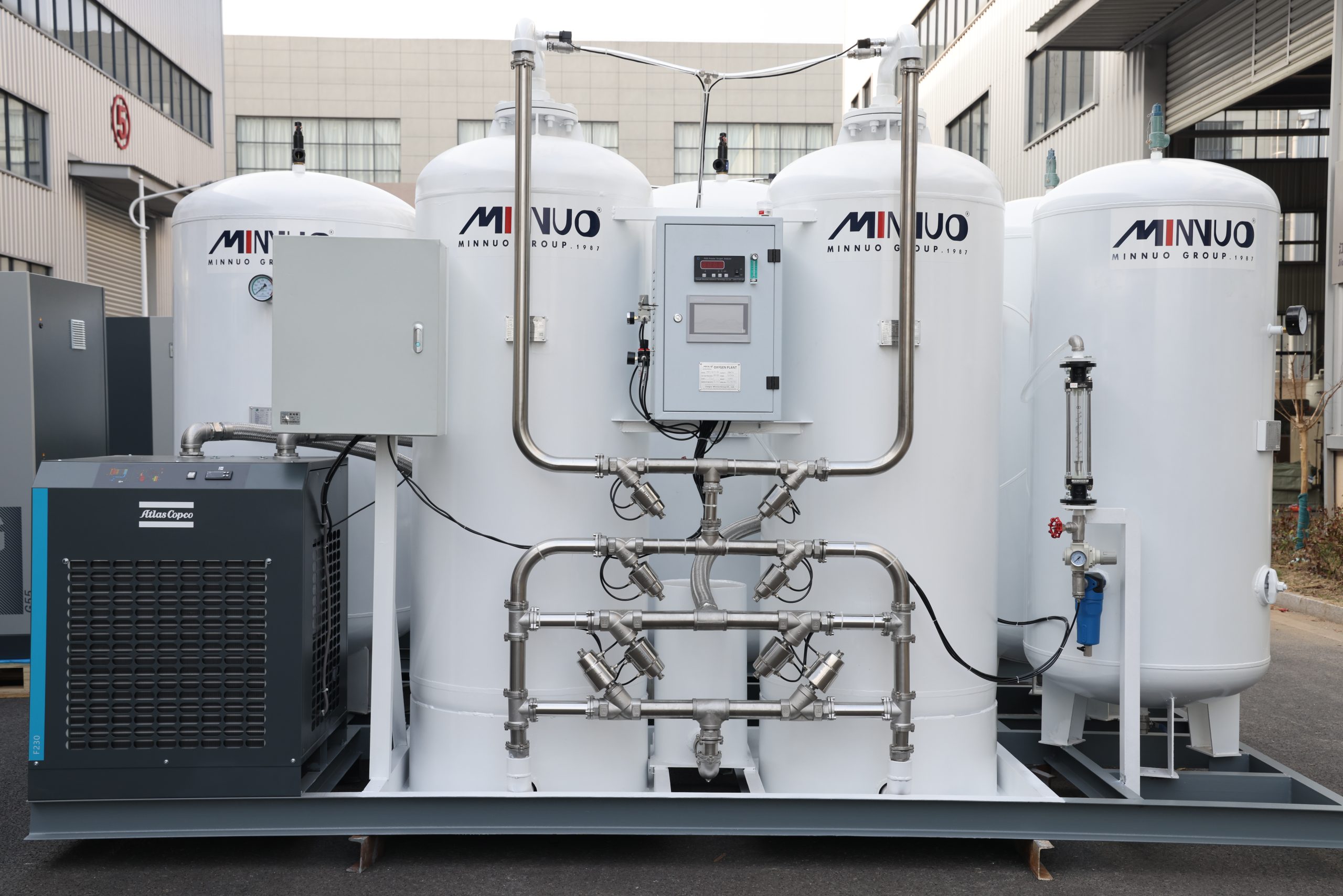
II. Key Components of Industrial Nitrogen Generators (and Maintenance Focus)
Before diving into maintenance, understanding core components helps identify high-wear parts and priority checks:
1. Air Compressor (Predecessor Equipment)
- Role: Supplies compressed air to the nitrogen generator (core input).
- Maintenance Focus: Filter cleaning/replacement, oil level checks (oil-injected models), and pressure stability.
2. Air Treatment System (Dryers & Filters)
- Role: Removes moisture, oil, and particulates from compressed air (contaminants damage generator membranes/adsorbents).
- Components: Refrigerated/desiccant dryers, pre-filters, coalescing filters.
- Maintenance Focus: Filter element replacement, dryer regeneration checks, drain valve cleaning.
3. Nitrogen Generation Core
- Membrane Generators: Hollow fiber membranes that separate nitrogen from air.
- PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) Generators: Carbon molecular sieves (CMS) that adsorb oxygen and other gases.
- Maintenance Focus: Membrane integrity checks, CMS bed condition, pressure differential monitoring.
4. Storage & Distribution System
- Role: Stores nitrogen in tanks and delivers it to industrial processes.
- Components: Storage tanks, pressure regulators, pipelines, and valves.
- Maintenance Focus: Tank pressure checks, leak detection, valve lubrication.
5. Control Panel & Sensors
- Role: Monitors nitrogen purity, pressure, and flow; triggers alarms for abnormalities.
- Maintenance Focus: Sensor calibration, control panel cleaning, software updates (for smart models).
III. Daily Maintenance Checklist (5–10 Minutes/Day)
Daily checks prevent minor issues from escalating into major failures. Focus on quick, high-impact inspections:
- Visual & Operational Checks
- Verify the nitrogen generator is running without abnormal noises, vibrations, or leaks.
- Check pressure gauges (inlet air pressure, nitrogen outlet pressure) for stability (within manufacturer-specified ranges).
- Inspect the control panel for error codes or alarm indicators (address immediately if triggered).
- Moisture & Drainage Checks
- Ensure automatic drain valves (in air dryers, filters, and storage tanks) are functioning—manually drain if buildup is visible.
- Check desiccant dryer indicators (if applicable): replace desiccant if it turns from blue to pink (sign of saturation).
- Purity Monitoring
- Confirm nitrogen purity meets process requirements (via on-site sensors or periodic lab tests).
- Note any sudden drops in purity (indicates membrane/CMS degradation or air treatment failures).
- Air Compressor Support Checks
- Inspect air compressor oil levels (oil-injected models) or filter status (oil-free models).
- Ensure compressor intake filters are clean (clogged filters reduce airflow and generator efficiency).
IV. Weekly Maintenance Tasks (30 Minutes/Week)
Weekly maintenance deepens daily checks and targets components prone to gradual wear:
- Filter Maintenance
- Clean or replace air intake pre-filters (for both the air compressor and nitrogen generator).
- Inspect coalescing filters for oil buildup—replace if the filter element is discolored or clogged.
- System Leak Detection
- Use a soapy water solution to check pipelines, valves, and fittings for leaks (bubbles indicate leakage).
- Tighten loose connections or replace worn gaskets/seals promptly (leaks reduce pressure and waste energy).
- Cooling System Checks
- For water-cooled generators: Inspect cooling water flow and temperature (keep within 20–30°C).
- For air-cooled generators: Clean cooling fins of dust and debris (blockages cause overheating).
- CMS/Membrane Condition Checks
- Monitor pressure differentials across the generation core (excessive differential = clogging or degradation).
- Ensure PSA generators complete full adsorption/desorption cycles (interrupted cycles reduce purity).

V. Monthly Maintenance Tasks (1–2 Hours/Month)
Monthly tasks focus on component integrity and performance calibration:
- Filter Replacement
- Replace pre-filters, coalescing filters, and carbon filters (follow manufacturer guidelines—typically every 1–3 months for industrial use).
- Use only OEM or compatible filters to avoid damaging the generator core.
- Sensor Calibration
- Calibrate nitrogen purity sensors, pressure transducers, and flow meters (inaccurate sensors lead to poor process control).
- Test alarm systems to ensure they trigger at preset thresholds (e.g., low purity, high pressure).
- Lubrication (Where Applicable)
- Lubricate valves, hinges, and moving parts of the storage tank (use manufacturer-recommended lubricants).
- For oil-injected air compressors: Replace oil if it appears discolored or contaminated.
- Membrane/PSA System Maintenance
- For membrane generators: Check for membrane damage (e.g., tears, blockages) and ensure proper airflow distribution.
- For PSA generators: Inspect CMS bed seals and replace if worn (leaks between beds reduce separation efficiency).
VI. Quarterly & Annual Maintenance (Professional-Grade)
Quarterly and annual tasks require specialized tools or technician expertise—critical for long-term reliability:
1. Quarterly Maintenance
- Deep clean the air treatment system: Disassemble and clean dryer coils, replace desiccant in desiccant dryers.
- Inspect the nitrogen storage tank: Check for corrosion (internal and external) and test pressure relief valves.
- Analyze nitrogen purity via third-party lab tests (validate on-site sensor accuracy).
2. Annual Maintenance
- Replace high-wear components: Membrane modules (every 5–7 years), CMS beds (every 3–5 years), and pressure regulators.
- Overhaul the air compressor: Replace compressor oil, filters, and gaskets; inspect piston rings and cylinders.
- Perform a full system performance test: Measure flow rate, purity, and energy consumption against baseline values.
- Update control panel software (for smart generators) to access latest diagnostic features.

VII. Common Nitrogen Generator Faults & Troubleshooting
Even with regular maintenance, industrial nitrogen generators may encounter issues. Below are frequent problems and solutions:
1. Low Nitrogen Purity
- Causes: Contaminated air input (moisture/oil), membrane/CMS degradation, incomplete PSA cycles, leaky pipelines.
- Solutions: Replace air treatment filters, regenerate or replace desiccant, inspect membrane/CMS for damage, repair leaks.
2. Reduced Flow Rate
- Causes: Clogged air filters, air compressor malfunction, pressure regulator issues, blocked pipelines.
- Solutions: Clean/replace filters, service the air compressor, calibrate regulators, clear pipeline blockages.
3. System Overheating
- Causes: Clogged cooling fins, malfunctioning cooling system, excessive ambient temperature, overloaded operation.
- Solutions: Clean cooling fins, repair water/air cooling systems, improve ventilation, reduce load to match generator capacity.
4. Alarm Triggers (Low Purity/Pressure)
- Causes: Sensor malfunction, system leaks, air supply failure, component wear.
- Solutions: Calibrate or replace sensors, detect and repair leaks, troubleshoot the air compressor, replace worn parts.
5. High Energy Consumption
- Causes: Leaks, inefficient air treatment, dirty filters, outdated components.
- Solutions: Fix leaks, upgrade to high-efficiency filters/dryers, clean or replace clogged parts, replace old membranes/CMS.
VIII. Maintenance Safety Guidelines
Industrial nitrogen generators operate at high pressure—follow these safety rules during maintenance:
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Disconnect power and relieve system pressure before disassembling any components.
- PPE (Personal Protective Equipment): Wear safety glasses, gloves, and ear protection (for noisy operations).
- Nitrogen Hazards: Avoid confined space exposure to nitrogen (it displaces oxygen)—ensure proper ventilation.
- OEM Guidelines: Never deviate from manufacturer maintenance procedures (use OEM parts and tools).
- Training: Only trained personnel should perform maintenance—avoid DIY repairs for complex issues (e.g., membrane replacement).
FAQs About Nitrogen Generator Maintenance
Q1: How often should I replace the carbon molecular sieve (CMS) in a PSA nitrogen generator?
A1: Typically every 3–5 years for industrial use. Factors like air quality, operating hours, and purity requirements affect lifespan—replace sooner if purity drops below specifications.
Q2: Can I use non-OEM filters for my nitrogen generator?
A2: Not recommended. Non-OEM filters may not remove contaminants effectively, leading to membrane/CMS damage and reduced equipment lifespan.
Q3: What’s the ideal ambient temperature for a nitrogen generator?
A3: 15–35°C. Extreme temperatures (below 10°C or above 40°C) reduce efficiency and can damage components like membranes and dryers.
Q4: How do I know if my nitrogen generator has a leak?
A4: Signs include reduced pressure, increased energy consumption, and inconsistent flow rates. Use a soapy water solution or ultrasonic leak detector to locate leaks in pipelines and valves.
Q5: Do membrane nitrogen generators require different maintenance than PSA models?
A5: Yes—membrane models focus on air quality (moisture/oil removal) and membrane integrity, while PSA models require CMS bed maintenance and cycle calibration. Both need regular air treatment system upkeep.
Conclusion
Proactive maintenance is the key to keeping industrial nitrogen generators running reliably, efficiently, and safely. By following daily, weekly, monthly, and annual maintenance schedules, you can avoid costly downtime, maintain nitrogen purity, and extend equipment lifespan.
Remember to prioritize air treatment (clean, dry air is critical for generator health), monitor key metrics (purity, pressure, flow), and address issues promptly. For complex maintenance tasks or troubleshooting, partner with certified technicians to ensure compliance with industrial standards.
Whether your nitrogen generator is used for food packaging, electronics manufacturing, or oil & gas operations, consistent maintenance transforms it from a piece of equipment into a reliable asset that supports seamless production and product quality. For MINNUO nitrogen generator users, following these practices aligns with our equipment’s engineered durability—paired with our OEM parts and dedicated after-sales support, you can maximize uptime and get the most out of your investment for years to come.






 sales2:+86 17506119168
sales2:+86 17506119168

