Nitrogen is a vital gas element found in the air. Despite its common presence, many people have limited knowledge about it. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of nitrogen, including essential facts you need to know about its composition, color, mass, and density.

| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 28.0134 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | Molecular Nitrogen |
| Color & Odor | Colorless, Odorless |
| Boiling Point | -195.795 °C |
| Melting Point | -210.00 °C |
Physical & Chemical Properties of N2
Understanding the fundamental properties of nitrogen gas is essential for its safe and effective use in various applications. Nitrogen (N2) is a unique element that makes up about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere.
Is Nitrogen Gas a Molecule?
Yes, nitrogen gas exists as a diatomic molecule. In its natural state, two nitrogen atoms are bound together by an extremely strong triple covalent bond (N≡N), which explains its high stability and inert nature. This molecular structure is why it is represented by the nitrogen gas formula: N2.
Key Physical Characteristics
- Color of Nitrogen Gas: Nitrogen is a completely colorless gas. It does not absorb or reflect visible light, making it invisible to the naked eye.
- Odor and Taste: It is entirely odorless and tasteless, which is why specialized sensors are required to detect its presence in confined spaces.
- Molecular Weight: The nitrogen molecular weight is 28.0134 g/mol, making it slightly lighter than the average weight of air.
- Solubility: It has low solubility in water, which is a critical factor in environmental and biological nitrogen cycles.
- Chemical Reactivity: At room temperature, N2 is largely inert. However, under high temperatures or pressures (such as in an engine or via the Haber process), it can react to form compounds like nitrogen oxides or ammonia.
Industrial Applications & Buying Guide
Because nitrogen is non-reactive and abundant, it is one of the most widely used industrial gases in the world. Transitioning from understanding “what is nitrogen” to knowing “how to use it” is key for professional procurement.
Common Industrial Uses
- Food Packaging (MAP): Nitrogen is used to “flush” oxygen out of food packaging (like potato chip bags). This prevents oxidation and spoilage, significantly extending shelf life without chemical preservatives.
- Electronics Manufacturing: In soldering and semiconductor fabrication, nitrogen creates an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation of delicate components.
- Medicine & Healthcare: Liquid nitrogen is famously used in cryotherapy to remove skin lesions and in laboratories to preserve biological samples like cells and tissues.
- Metal Processing: Used in laser cutting and heat treating to ensure a clean finish on stainless steel and aluminum by preventing contact with oxygen.
Buying Guide: How to Source Nitrogen Gas
When looking to buy nitrogen gas, consider the following factors to ensure you get the right product for your specific industry:
- Purity Levels: Do you need Industrial Grade (99.5%), High Purity (99.99%), or Ultra-High Purity (99.999%)? Food and medical applications typically require higher purity standards.
- Supply Mode: * Cylinders: Best for low-volume or portable needs.
- Dewars: Used for liquid nitrogen storage.
- On-site Generators: Ideal for high-volume, continuous industrial consumption to save on long-term costs.
- Safety Compliance: Ensure your supplier provides MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) and that your facility has proper ventilation and oxygen depletion alarms.
Definition: What is Nitrogen Gas
At room temperature and normal pressure, nitrogen is a colorless, odorless gas and a simple substance formed by nitrogen elements. It makes up 78% of the air, making it the most abundant gas in the atmosphere. Because of this, we have an unlimited supply of nitrogen.
Physical Properties of Nitrogen Gas
Color:
Do you know the color of nitrogen gas? Look at the air around us; it’s colorless, right? Nitrogen is a colorless gas, always present around us, yet invisible.
Mass:
A nitrogen molecule consists of two nitrogen atoms. To determine its mass, consider the combined mass of these two atoms. In the International System of Units (SI), the atomic mass of a nitrogen atom is 14.007 u (atomic mass units). Therefore, the mass of a nitrogen molecule is 28.01 u, equivalent to 28.01 g.
Molar Mass:
The unit for the amount of substance is the mole (mol). The molar mass of nitrogen, which is the mass of a substance divided by the amount of substance, is 28.01 g/mol.
Density of Nitrogen Gas:
Gas density typically refers to the density of the gas at standard temperature (273.15K). It depends on the molecular weight of the gas, temperature, and pressure. Given nitrogen’s molecular weight of 28.01 g/mol, we use the ideal gas law PV=nRT (where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature) and the formula for density, density = mass/volume. At standard conditions (pressure = 1 atm, volume of 1 mole of gas = 22.4 L, temperature = 273.15K), the density of nitrogen is calculated as:
density=22.4L/mol28.01g/mol=1.25g/L
This means the density of nitrogen at standard temperature is 1.25 g/L or 1.25 kg/m³.
Pressure:
Using the ideal gas law, we can determine that at standard room temperature (25°C), the pressure of nitrogen gas is 101.325 kPa.
Temperature:
What is the temperature of nitrogen gas? The state of nitrogen changes with temperature. At room temperature, nitrogen gas is at 25°C. When cooled to -196°C, it becomes a liquid (liquid nitrogen). At -209°C, liquid nitrogen solidifies into a snow-like solid. Whether nitrogen is in a solid, liquid, or gaseous state depends entirely on its current temperature.
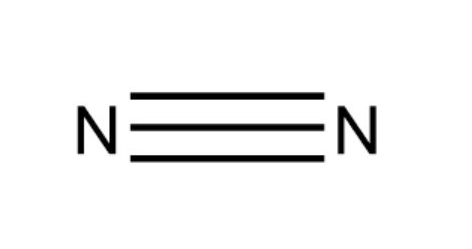
Chemical Properties of Nitrogen Gas
Nitrogen is an inert gas that generally does not react with other substances, making it commonly used as a preservative.
Chemical Symbol
N₂
Specific Conditions
Under certain conditions such as high temperature, high pressure, or electrical discharge, nitrogen can react with some elements or compounds.
- Reaction with Hydrogen: At high temperatures, nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia (NH₃).
- Reaction with Oxygen: Under electrical discharge or high temperature, nitrogen reacts with oxygen to produce nitric oxide (NO).
- Reaction with Magnesium: Nitrogen reacts with magnesium when ignited to form magnesium nitride.
- Reaction with Reactive Metals: Nitrogen also reacts with certain reactive metals like calcium, magnesium, strontium, and barium when heated.
Q: What is the chemical formula for nitrogen gas?
A: The chemical formula for nitrogen gas is N2, representing two nitrogen atoms bonded together.
Q: What is the molecular weight of nitrogen?
A: The molecular weight (molar mass) of nitrogen gas (N2) is approximately 28.014 g/mol.
Q: Is nitrogen gas flammable?
A: No, nitrogen gas is an inert, non-flammable gas often used for purging and blanketing.
Summary
In summary, we have explored the physical and chemical properties of nitrogen to understand what initrogen gas is. For more information about nitrogen, you can refer to the “Ultimate Guide to Nitrogen Generators.“
Need Reliable Nitrogen Gas Supply?
We provide high-purity nitrogen for various industrial needs. [Browse Our Nitrogen Products] | [Get a Quick Quote]








 sales2:+86 17506119168
sales2:+86 17506119168

